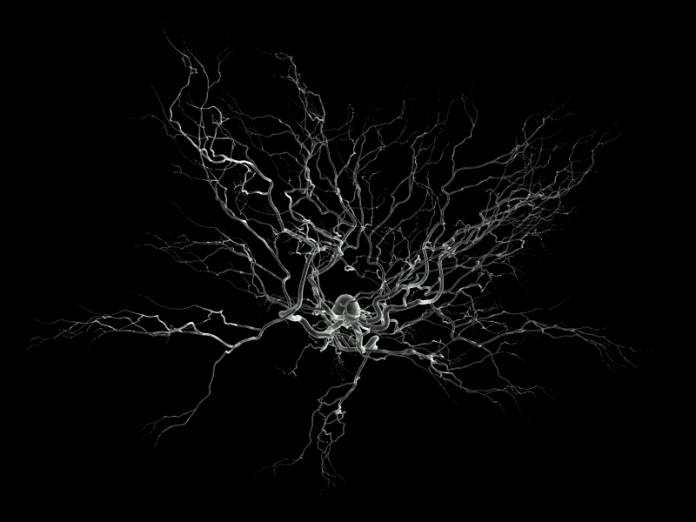
Scientists have developed a 3D bioprinting platform that assembles functional uman neural tissues. The progenitor cells in the printed tissues grow to form neural circuits and make functional connections with other neurons thus mimicking natural brain tissues. This is a significant progress in neural tissue engineering and in 3D bioprinting technology. Such bioprinted neural tissues can be used in modelling uman diseases (such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s etc.) caused due to impairment of neural networks. Any investigation of disease of brain requires understanding how the uman neural networks operate.
Bioprintare 3D este un proces aditiv în care biomaterialul natural sau sintetic adecvat (biocerneală) este amestecat cu celule vii și imprimat, strat cu strat, în structuri tridimensionale asemănătoare țesuturilor naturale. Celulele cresc în biocerneală, iar structurile se dezvoltă pentru a imita țesutul sau organul natural. Această tehnologie și-a găsit aplicații în regenerator medicine for bioprinting of cells, tissues and organs and in research as model to study uman corp in vitro, în special uman sistem nervos.
Studii de uman nervous system faces limitations due to unavailability of primary samples. Animal models are helpful but suffer from species-specific differences hence the imperative of in vitro modele de uman nervous system to investigate how the uman neural networks operate towards finding treatments for diseases attributed to impairment of neural networks.
Uman neural tissues have been 3D printed in the past using stem cells however these lacked neural network formation. The printed tissue had not shown to have formed connections between cells for several reasons. These shortcomings have been overcome now.
In a recent study, researchers chose fibrin hydrogel (consisting of fibrinogen and thrombin) as the basic bioink and planned to print a layered structure in which progenitor cells could grow and form synapses within and across layers, but they changed the way layers are stacked during printing. Instead of traditional way of stacking layers vertically, they chose to print layers next to another horizontally. Apparently, this made the difference. Their 3D bioprinting platform was found to assemble functional uman neural tissue. An improvement over other existing platforms, the uman neural tissue printed by this platform formed neural networks and functional connections with other neurons and glial cells within and between layers. This is the first such case and is a significant step forward in neural tissue engineering. Laboratory synthesis of nerve tissue that mimics brain in function sounds exciting. This progress will certainly help researchers in modelling uman diseases of brain caused due to impaired neural network to better understand the mechanism for finding a possible treatment.
***
Referinte:
- Cadena M., et al 2020. Bioprinting 3D a țesuturilor neuronale. Materiale avansate de îngrijire medicală Volumul 10, Numărul 15 2001600. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202001600
- Yan Y., et al 2024. 3D bioprinting of uman neural tissues with functional connectivity. Cell Stem Cell Technology| Volume 31, Issue 2, P260-274.E7, February 01, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2023.12.009
***